|
Ebola virus disease (EVD), Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF) or simply Ebola is a disease of humans and other mammals caused by ebola virus.
Signs and symptoms
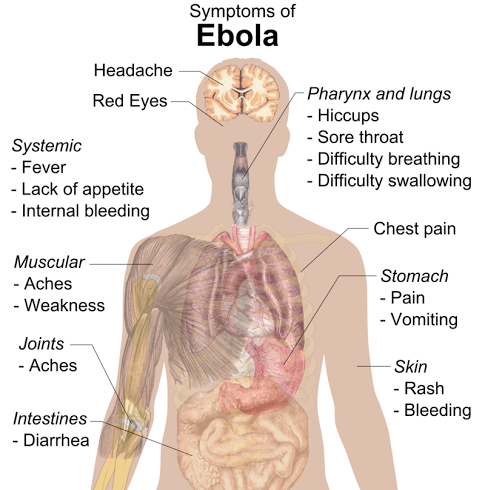
Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus, with a fever, sore throat, muscle pain and headaches. Then, vomiting, diarrhea and rash usually follow, along with decreased function of the liver and kidneys. Around this time, infected people may begin to bleed both within the body and externally. Death, if it occurs, is typically six to sixteen days after symptoms appear and is often due to low blood pressure from fluid loss.
Transmission of Diesease
The virus is acquired by contact with blood or other body fluids of an infected human or other animal. This may also occur by direct contact with a recently contaminated item. Spread through the air has not been documented in the natural environment. Fruit bats are believed to be the normal carrier in nature, able to spread the virus without being affected. Humans become infected by contact with the bats or a living or dead animal that has been infected by bats. Once human infection occurs, the disease may spread between people as well. Male survivors may be able to transmit the disease via semen for nearly two months. To diagnose EVD, other diseases with similar symptoms such as malaria, cholera and other viral hemorrhagic fevers are first excluded. Blood samples are tested for viral antibodies, viral RNA, or the virus itself to confirm the diagnosis.
|
Saturday, 18 October 2014
ebola, What is EVD
What is EVD ??
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)










0 comments:
Post a Comment